
Fabric Expansion Joints
Fabric expansion joints provide an effective and reliable solution to compensate for thermal expansion, mechanical movements, and vibrations in piping and duct systems. Our high-quality fabric expansion joints are used in a wide range of industrial applications, including power plants, chemical plants, refineries, cement plants, and many other areas where high temperatures and demanding operating conditions prevail.
Our fabric expansion joints are made from special, temperature-resistant, and durable fabric layers that are configured according to the specific requirements of our customers. The choice of materials depends on the medium, temperature, and pressure of the application. Materials used include E-glass fibers, silica fibers, and PTFE-coated fabrics, which are processed with or without graphite inserts as a sealing layer. For applications involving extreme temperatures, we also offer insulation layers made of high-performance silica fabrics, as well as EPDM-coated fabrics for particularly high mechanical requirements or outdoor use.
| Material | Temperature-resistant glass fabrics |
| Maximum operating temperature | up to 900°C |
| Design | Custom-made and application-oriented |
Movements
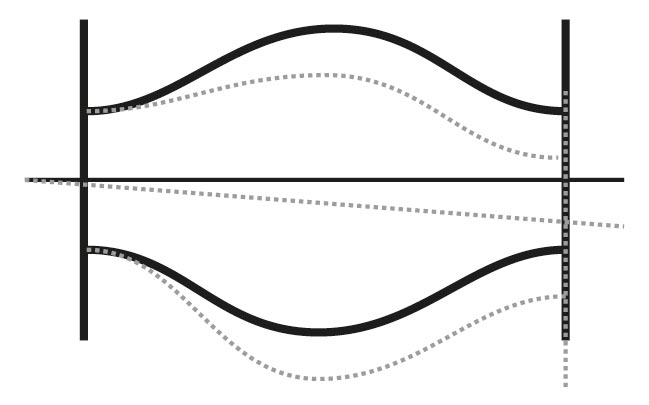
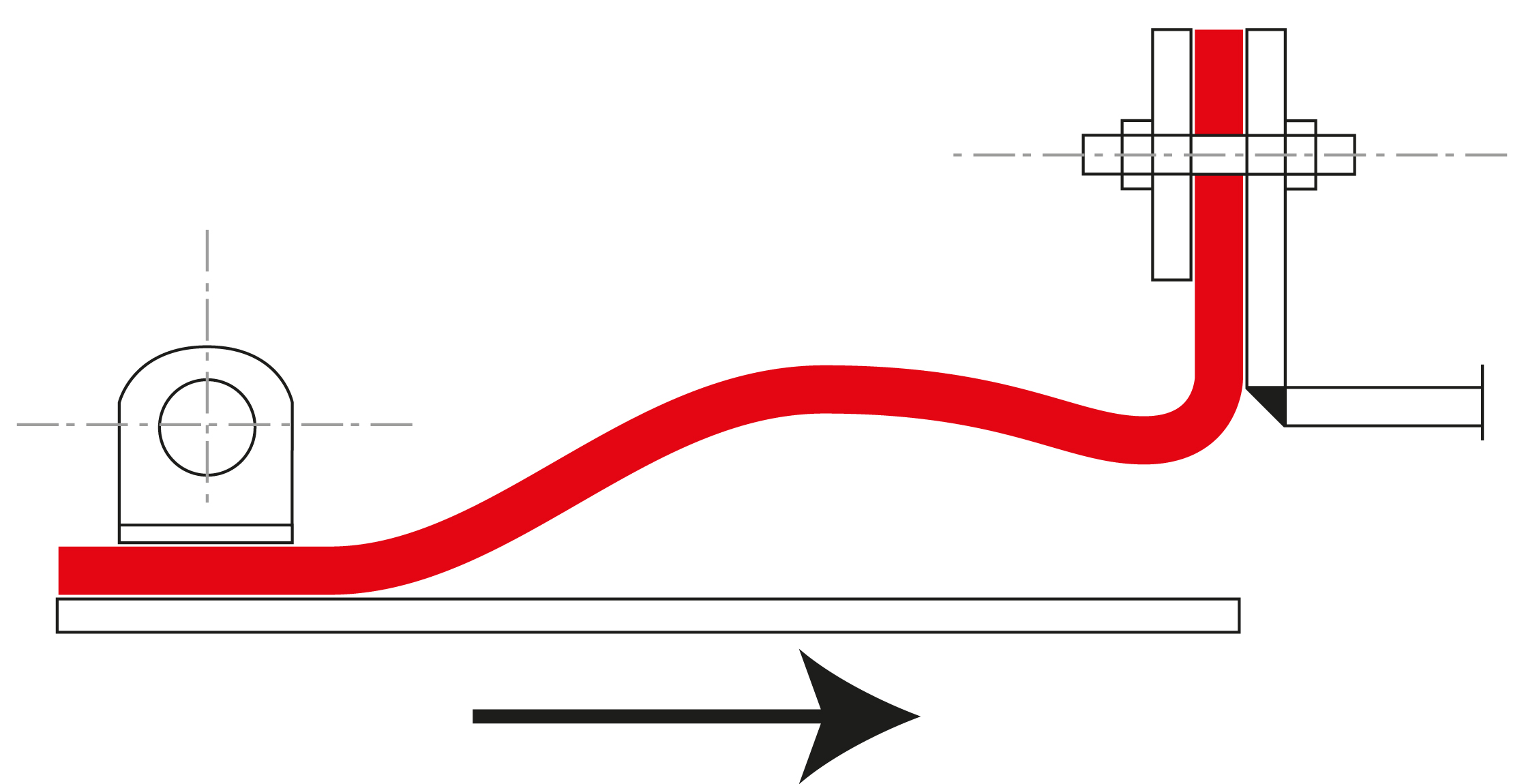
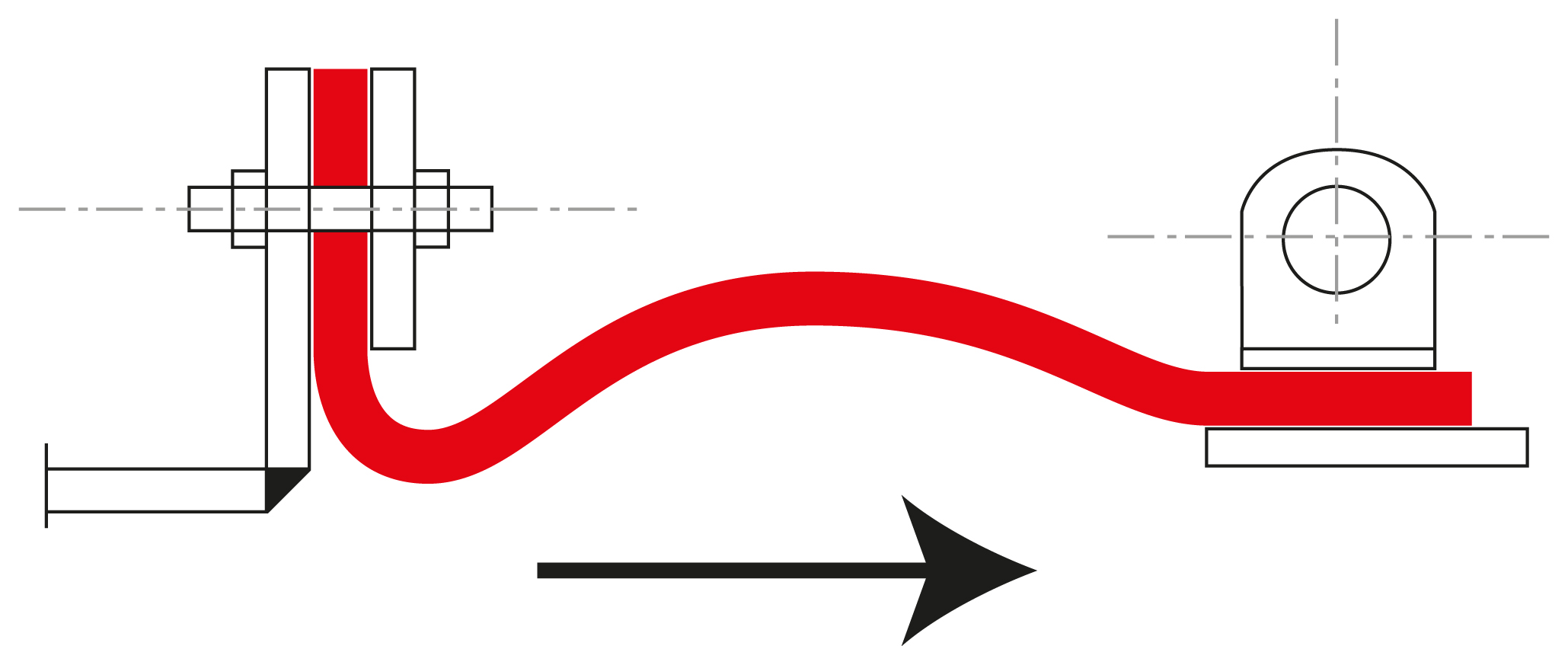
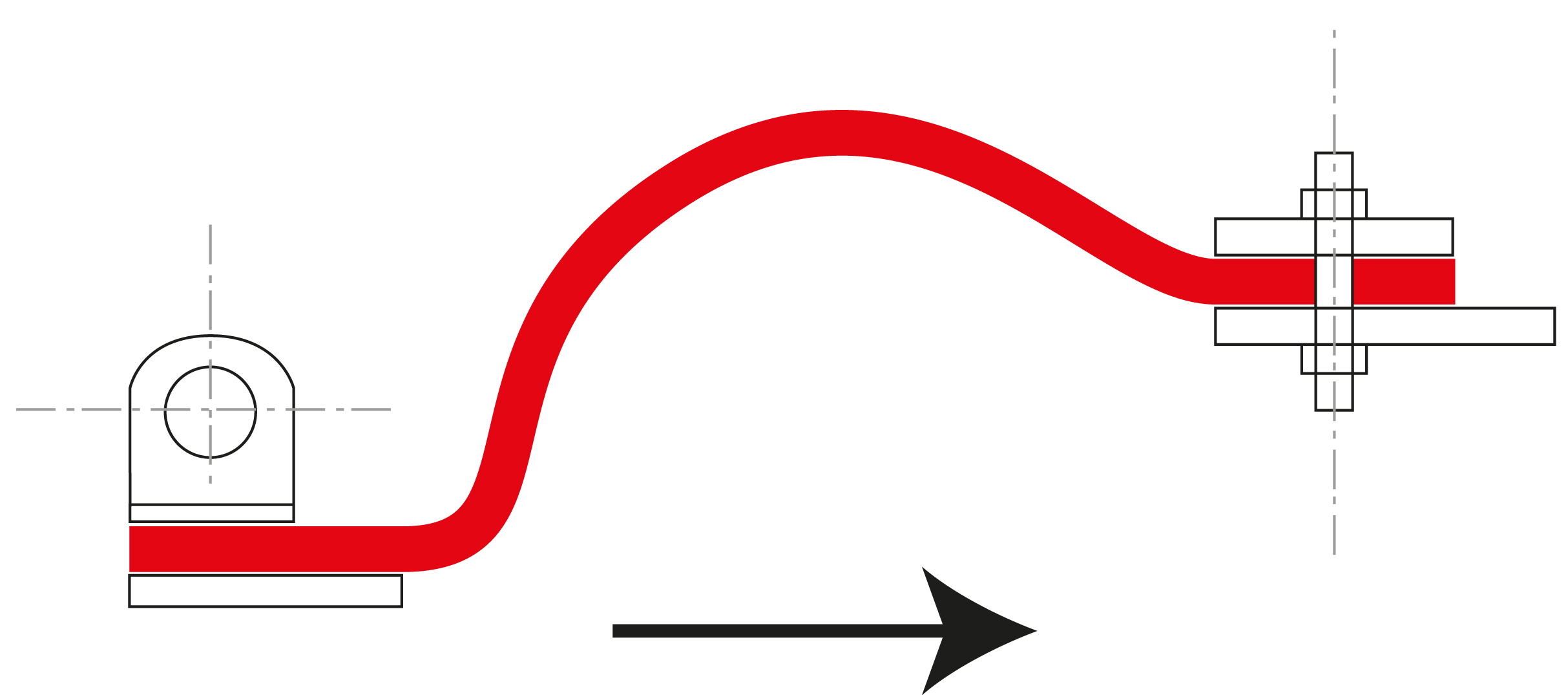
Axial movement (expansion and compression): Axial movement absorption refers to movements along the longitudinal axis of the pipeline. When temperatures change, pipelines expand or contract. Fabric expansion joints compensate for this expansion or compression by flexibly responding to the length changes. This is particularly important in high-temperature applications, where significant thermal expansion can occur.
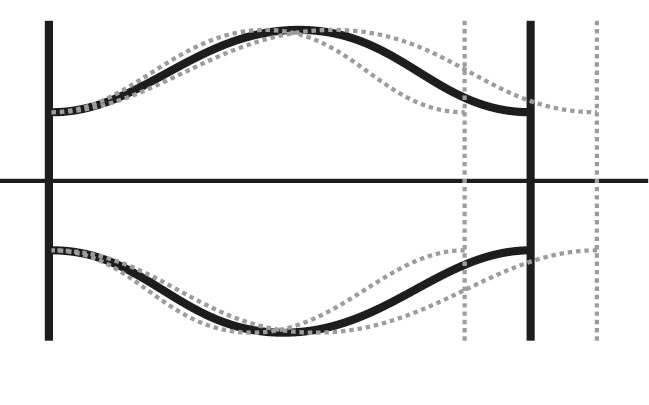
Lateral movement (displacement): Lateral movements occur when two adjacent sections of a pipeline shift sideways relative to each other. Fabric expansion joints can absorb these transverse movements, preventing damage or deformation. Lateral movement absorption is particularly important in complex piping systems, where the pipes can be displaced due to external influences, such as vibrations.
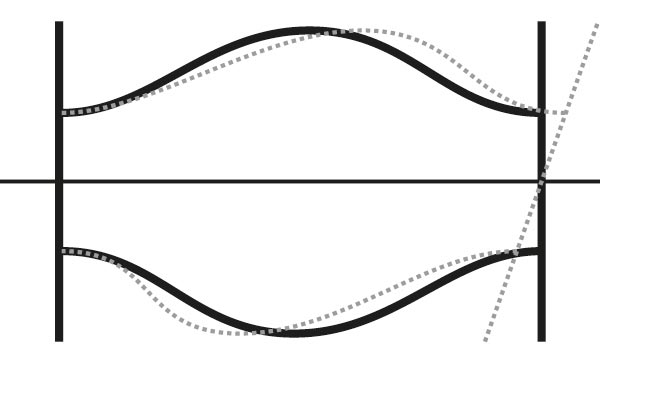
Angular movement (rotation): Angular movement absorption allows for the compensation of rotational movements between two pipelines or components. When pipeline elements move at a certain angle relative to each other, the fabric expansion joint ensures that these angular changes are absorbed without stress compensation. This prevents damage to the pipelines or the expansion joint itself.
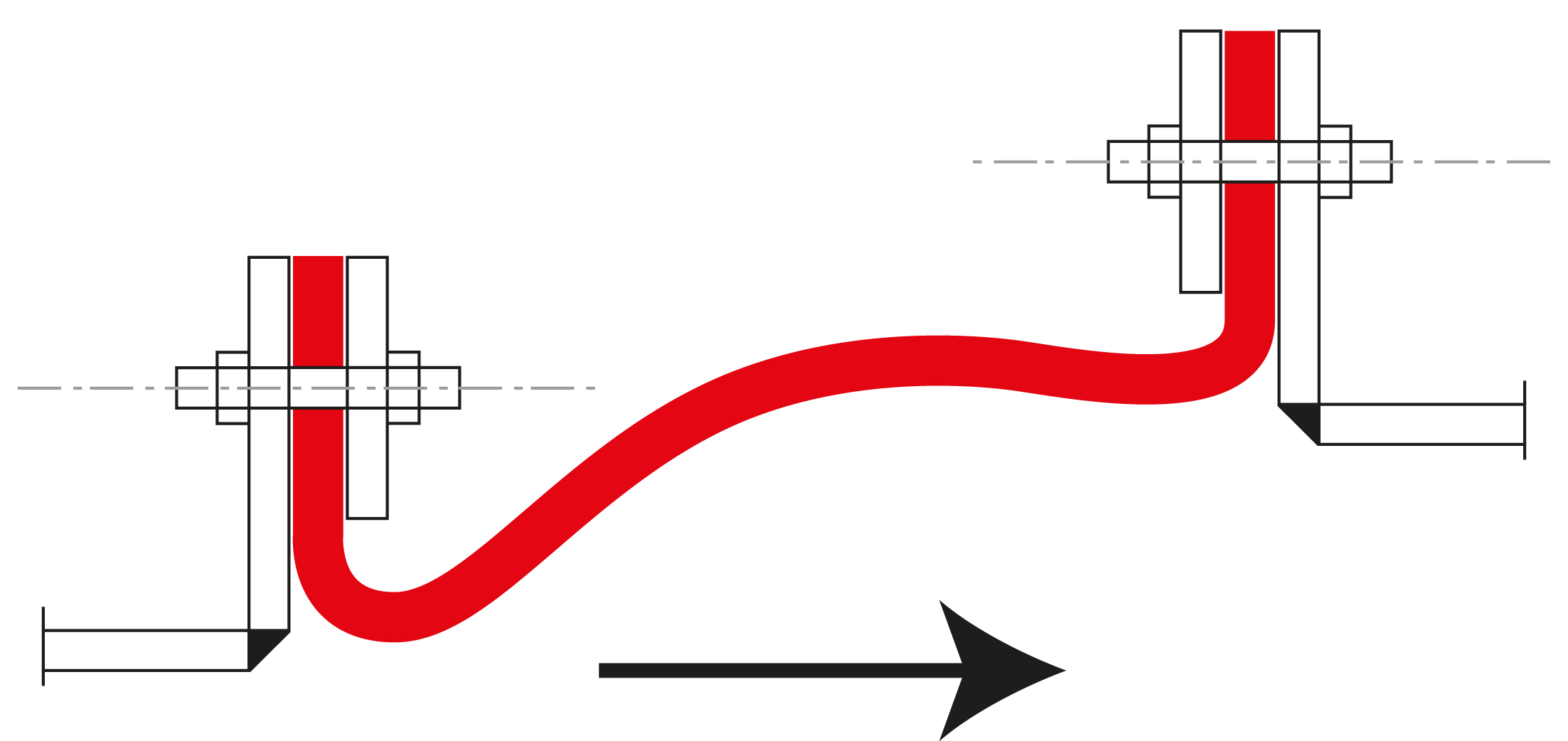
Mounting options
Flange mounting: One of the most commonly used fastening methods is flange mounting. In this method, the fabric expansion joint is installed and bolted between two flanges. This method provides a strong, secure connection and is particularly suitable for systems with high pressure or in applications where tightness and stability are of central importance.
Clamp bar installation: In this fastening method, the expansion joint is secured using clamp bars. The clamp bars allow for quick and easy installation by clamping the fabric expansion joint onto the edges of the pipes or ducts. This method is ideal for applications requiring frequent maintenance or inspections, as it allows for easy disassembly.
Clamp fastening with tension bands: In flexible and dynamic applications where the expansion joint is subjected to frequent movements or vibrations, clamp fastening with tension bands can be used. This method ensures that the expansion joint remains securely in place while compensating for movements and vibrations within the system.
Technical Characteristics
- Suitable for applications with temperatures ranging from -50°C to +900°C (depending on the materials and coatings used).
- Suitable for low-pressure applications up to approximately 0.25 bar.
- High flexibility to absorb axial, lateral, and angular movements caused by thermal expansion or mechanical influences.
- Manufactured from high-quality and durable materials such as E-glass fiber fabrics, silica fiber fabrics, PTFE-coated fabrics, and EPDM-coated fabrics.
- Individually customizable and process-oriented coatings made from aluminum, PTFE, silicone, or other heat-resistant materials.
- High resistance to aggressive media, chemicals, and moisture.
- Reduction of structure-borne noise transmission and vibrations to lower the noise level in the facility.
- Fabric expansion joints made from special materials provide protection against corrosive environments.
- Suitable for ATEX-protected environments (expansion joints up to 250°C).
Application Examples
- Power plants (steam, gas, nuclear): Compensation for thermal expansion and vibrations in exhaust ducts, flue gas dedusting systems, or during the discharge of hot air and gases.
- Cement plants: Compensation for movements in high-temperature exhaust ducts that are exposed to significant thermal stress in the kiln area.
- Oil and gas industry: Fabric expansion joints are used in refineries and petrochemical plants to absorb movements in pipes and ducts exposed to high temperatures and aggressive media.
- Steel industry: Compensation for movements in flue gas ducts and dedusting systems, where high temperatures and strong mechanical forces are present.
- Waste incineration plants: Used in flue gas disposal systems to absorb thermal expansion and prevent vibrations in hot gas ducts.
- Automotive industry: Used in exhaust disposal systems and in facilities where high thermal stresses occur, such as in production lines for engines or exhaust systems.
- Aerospace engineering: Protection against extreme temperatures and vibrations in high-temperature applications, such as hot air or exhaust systems in test stands.
Similar products














